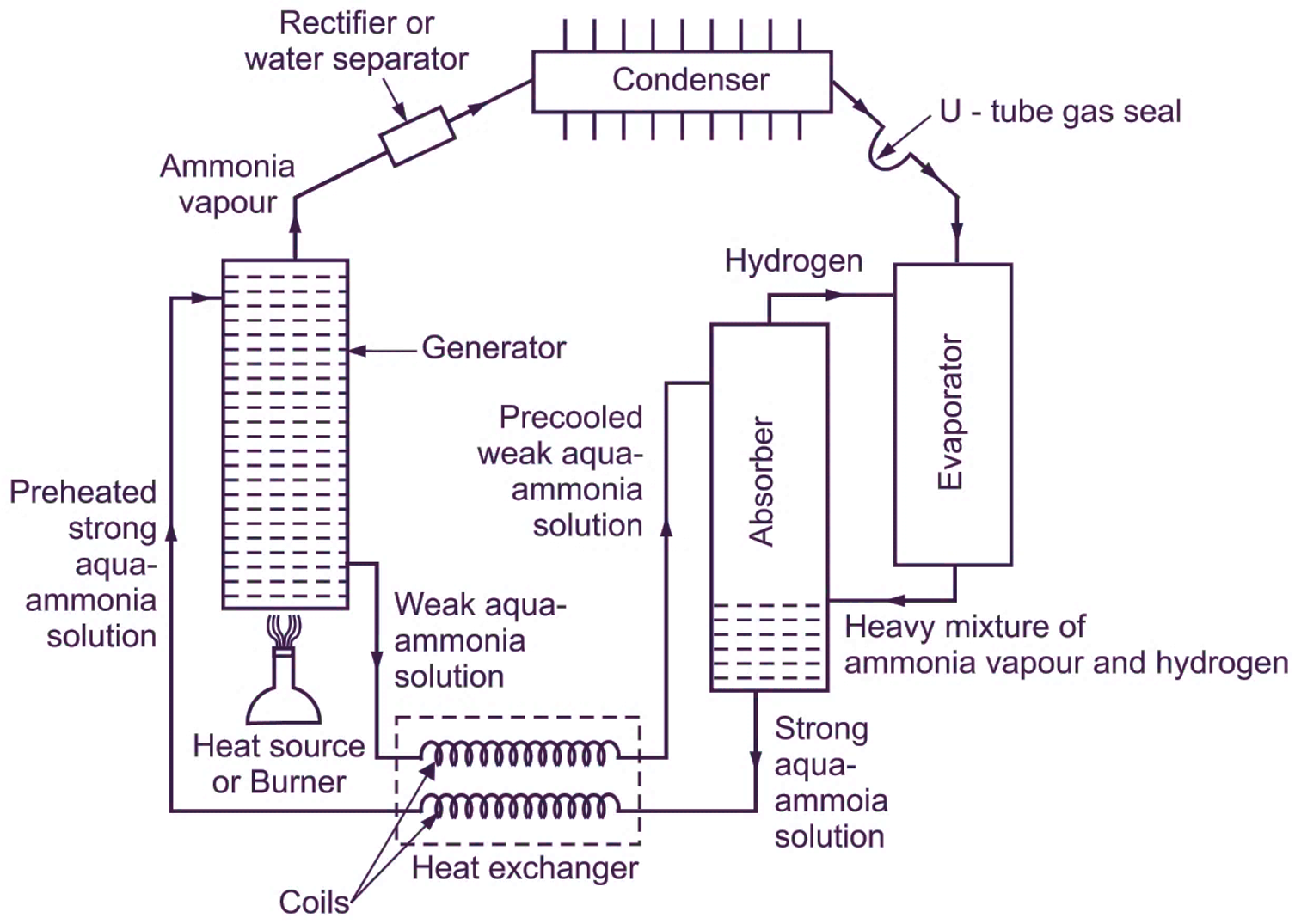
Main purpose of Electrolux Refrigerator: “To eliminate pump, absorption refrigeration system completely free from moving parts”. Electrolux Refrigerator is a three fluid refrigeration absorption system. It is also called as “NH3 – Hydrogen Refrigerator”. The three fluids used are, a refrigerant (Ammonia), a solvent (Water) and an inert gas (Hydrogen). These fluids are briefly described in the following manner.
Electrolux refrigerator makes the use of properties of gas-vapour mixtures (i .e. mixture of hydrogen gas and vapour refrigerant). If a liquid (here, liquid refrigerant ammonia) is exposed to an inert atmosphere (here, Hydrogen gas), then the liquid will evaporate. This evaporation requires heat, which is taken from the surroundings (here, space or substance to be cooled), in which, the evaporation takes place. A cooling effect is thus produced. The partial pressures of vapour refrigerant (here, Ammonia) must be low in the evaporator and high in condenser. The total pressure throughout the circuit must be constant, so that, the movement of the working fluid (here, ammonia as refrigerant) is purely by means of convection currents. Therefore, no pump is required for circulation and pressure increase. Partial pressure of working fluid (here, ammonia as refrigerant) is kept low in requisite parts of the circuit by concentrating hydrogen in those parts.
Strong aqua ammonia solution present in the absorber flows in to the generator. It is heated in the generator by using an external source like gas burner. During this heating process, the ammonia dissolved in the strong solution gets vapourized. This ammonia vapour refrigerant coming out from the generator is passed through a rectifier or water separator provided between the generator and the condenser. Sometimes, water vapours (in small quantity) may be formed in generator. These water vapours may pass on to condenser and then to evaporator along with ammonia vapours, where they may freeze at low temperature and further, may choke the tubes. The function of rectifier or water separator is to prevent the entry of these water vapours into condenser and then to the evaporator. After passing through rectifier, the dehydrated ammonia vapour is liquefied in the condenser. After condenser, a U-tube gas seal is provided to prevent backflow of ammonia as well as entry Of hydrogen in to the condenser. Now, liquid ammonia enters the evaporator, where it meets the hydrogen gas. Please note that, the whole system is charged to a pressure of 14 bar and the evaporator contains hydrogen at a pressure of 12 bar.
Therefore, as soon as, the liquid ammonia enters the evaporator, its pressure drops to 2 bar according to Dalton’s law of partial pressure, and its corresponding temperature being about -18°C. This liquid ammonia having very low temperature of -18°C (corresponding to partial pressure 2 bar) absorbs the heat (which is equal to its latent heat of vaporization from the space to be cooled (i.e. evaporator) and gets evaporated (i.e. phase change). This produces the desired cooling effect. This heavy mixture of ammonia vapour and hydrogen then passes into the absorber, where it meets the water (weak solution) coming from the generator. In the absorber, ammonia vapour gets absorbed in water, while hydrogen rises to the top of absorber and returns back to the evaporator. Due to absorption of NH3 vapours in water (weak solution), it becomes strong aqua ammonia solution. Thus, hydrogen carries ammonia to absorber, where ammonia is absorbed and hydrogen returns to evaporator. This strong aqua ammonia solution coming from the absorber is preheated in the heat exchanger, by absorbing heat from weak aqua ammonia solution. Thus, the weak aqua ammonia solution on its way to absorber gets cooled, thereby accelerating absorption. This completes the cycle. Note that, total pressure at every point in the system is same. It may also be noted that, in the above system, ‘hydrogen flows only from absorber to evaporator and back’. The Whole cycle is carried out by gravity flow of refrigerant (Figure 1). Therefore, pump can be eliminated from the system, which is used in other vapour absorption systems for circulation of refrigerant and for increasing the pressure of refrigerant. However, COP of this system is very low.

Fig. 1: Electrolux refrigerator
Role of Hydrogen in Electrolux Refrigerator
Hydrogen is non-corrosive and insoluble in water. Role of Hydrogen as
These conditions of pressures are achieved without use of pumps or valves.
What is Screw Compressor? Working, Construction & Diagram Screw compressor is also called as helical rotary compressor. Screw compressor is displacement compressor, in…
What is Winter Air Conditioning System? Construction & Working In winter, the atmosphere is generally cool and humid, i.e. near to 15°C dry bulb…
What is Automobile Air Conditioning System? Working, Construction & Diagram Capacity of automobile air conditioning systems: 1 TOR to 4 TOR. Refrigeration cycle used: Vapour…
What is Summer Air Conditioning System? Construction & Working Summer air conditioning system is used in two types of weather conditions. Hot and wet…
Autotransformer Starter - Working & Diagram In this topic, you study Autotransformer Starter - Working & Diagram. A three phase, star-connected…